Friday, 3 February 2012
Examples of white balance
What is white balance?
It all boils down to the concept of color temperature. Color temperature is a way of measuring the quality of a light source. It is based on the ratio of the amount of blue light to the amount of red light, and the green light is ignored. The unit for measuring this ratio is in degree Kelvin (K). A light with higher color temperature (i.e., larger Kelvin value) has "more" blue lights than a light with lower color temperature (i.e., smaller Kelvin value). Thus, a cooler (resp., warmer) light has a higher (resp., lower) color temperature.
The following table shows the color temperature of some light sources
It all boils down to the concept of color temperature. Color temperature is a way of measuring the quality of a light source. It is based on the ratio of the amount of blue light to the amount of red light, and the green light is ignored. The unit for measuring this ratio is in degree Kelvin (K). A light with higher color temperature (i.e., larger Kelvin value) has "more" blue lights than a light with lower color temperature (i.e., smaller Kelvin value). Thus, a cooler (resp., warmer) light has a higher (resp., lower) color temperature.
The following table shows the color temperature of some light sources
| Light Sources | Color Temperature in K |
| Clear Blue Sky | 10,000 to 15,000 |
| Overcast Sky | 6,000 to 8,000 |
| Noon Sun and Clear Sky | 6,500 |
| Sunlight Average | 5,400 to 6,000 |
| Electronic Flash | 5,400 to 6,000 |
| Household Lighting | 2,500 to 3,000 |
| 200-watt Bulb | 2,980 |
| 100-watt Bulb | 2,900 |
| 75-watt Bulb | 2,820 |
| 60-watt Bulb | 2,800 |
| 40-watt Bulb | 2,650 |
| Candle Flame | 1,200 to 1,500 |
Friday, 13 January 2012
Examples of Lighting - Hard and Soft Light
Uses of soft light
- Soft light use is popular in cinematography and film.
- Cast shadow-less light
- Fill lighting. Soft light can reduce shadows without creating additional shadows.
- Make a subject appear more beautiful or youthful through making wrinkles less visible.
- Supplement the lighting from practicals. This technique is used to perform "motivated" lighting, where all light in the scene appears to come from practical light sources in the scene. Soft light does not cast shadows that would be a giveaway of a supplementary light source.
Hard light
Hard light sources cast shadows whose appearance of the shadow depends on the lighting instrument. For example, fresnel lights can be focused such that their shadows can be "cut" with crisp shadows. That is, the shadows produced will have 'harder' edges with less transition between illumination and shadow. The focused light will produce harder-edged shadows. Focusing a fresnel makes the rays of emitted light more parallel. The parallelism of these rays determines the quality of the shadows. For shadows with no transitional edge/gradient, a point light source is required.
Here you can see the light changing.
Friday, 9 December 2011
Portrait Photography
Portrait photography is the capture by means of photography of the likeness of a person or a small group of people (a group portrait), in which the face and expression is focal point of the photo. The objective is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the subject.
Group Portraits
Here are a few of my portrait photos, even though two are of a animal to me it still counts as portrait, as its all about capturing the emotion with in the photo.
Tuesday, 6 December 2011
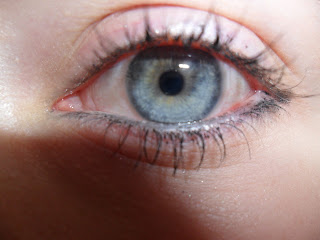
MACRO Photography
Macro Photography is close-up photography, usually of very small subjects. classically a macro photograph is one in which the subject on the negative is bigger than in life size. However in modern use it refers to a finished photograph of a subject as greater than life size.
Comparing macro with landscape, the main difference between them is that the aim of landscape is to show the bigger picture and to show lots of things. where as macro its of one main thing and showing all the detail of that.
MACRO
Landscape
Friday, 18 November 2011
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)